Remove “Confirm Your Identity” email
The “Confirm Your Identity” email is part of a phishing campaign that intends to steal users’ email login credentials, specifically their passwords. The email is made to appear as a security alert from your email service provider. It falsely informs you that verifying your identity is necessary to maintain access to your account. The email gives you 48 hours to verify your identity, after which your account will no longer receive or be able to send emails. The contents of this email are entirely false, and this is nothing more than a generic phishing attempt. If you were to click on the button in the email, you would be taken to a phishing site that asks you to log in to your email account. If you do as asked, your password would be sent to malicious actors operating the phishing campaign.
The “Confirm Your Identity” email claims that because of your email service provider’s new security measures, you need to verify your identity. According to the email, this is supposedly to ensure your data remains protected. This is a standard ruse used in many phishing emails. You are pressured to click on the provided link because if you do not verify your identity within 48 hours, your email account will supposedly stop receiving and being able to send emails.
The full “Confirm Your Identity” email:
Subject: Identity Verification For {-} On –
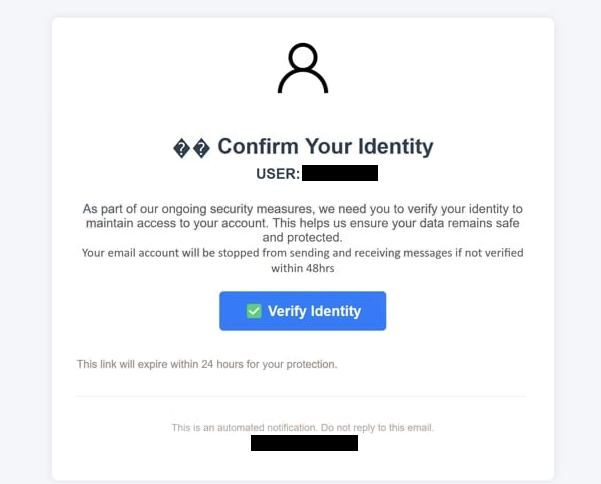
Confirm Your Identity
USER: –As part of our ongoing security measures, we need you to verify your identity to maintain access to your account. This helps us ensure your data remains safe and protected.
Your email account will be stopped from sending and receiving messages if not verified within 48hrsVerify Identity
This link will expire within 24 hours for your protection.
This is an automate notification. Do not reply to this email.
–
If you click on the provided “Verify Identity” button, you will be directed to a phishing site. This phishing site is imitating Gmail’s login page. Your username will already be typed in, and only the password field will be empty. Once the login information is provided, the credentials are immediately sent to the cybercriminals operating the phishing campaign. The malicious nature of the site is evident from its URL, which does not align with the official Gmail URL.
The stolen credentials may be exploited directly by the cybercriminals or sold to other malicious actors. Such information is very valuable to cybercriminals, as email accounts are often linked to multiple other accounts and can contain sensitive data. Successfully compromising an email account could grant cybercriminals access to associated accounts and confidential information.
How to recognize phishing emails?
Phishing campaigns that target a large number of users with the same emails are often generic and relatively easy to recognize as malicious. These emails typically lack credible details, frequently contain grammar and spelling mistakes, and appear unprofessional, which are all signs of a spam or malicious email. However, when phishing attempts are directed at specific individuals or companies, the emails can become highly sophisticated and may deceive even the most cautious users if the circumstances are right.
Generic phishing emails, such as the “Confirm Your Identity” email, usually have signs pointing to their being malicious. Firstly, they tend to look unprofessional and contain several grammar/spelling mistakes. Users should be on the lookout for grammar and spelling mistakes in unsolicited emails, as these are common indicators of malicious intent. Furthermore, the “Confirm Your Identity” email does not personally address the recipient. Instead, it uses the email username. Legitimate correspondence from an email service provider will always address users by name. In contrast, phishing or malicious emails often omit a greeting, use generic terms like “User,” “Member,” or “Customer,” or address users by their email username—all of which are typical red flags.
When dealing with unsolicited emails that require clicking on links or downloading attachments, users should pause and carefully consider whether the email contents make sense. For example, email server providers do not send users emails asking them to confirm their identities.
Finally, users should avoid clicking on links in emails altogether. Instead, users should manually log into their account through a browser rather than using any link provided in the email.
Remove “Confirm Your Identity” email
If you receive this “Confirm Your Identity” phishing email in your inbox, delete it immediately. If you have already interacted with the email and provided your email login credentials, it is crucial to change your password right away, assuming you still have access to your account. In the event your email account has been compromised, you should attempt all available account recovery options. If recovery proves unsuccessful, disconnect your email account from all linked accounts to protect them from potential unauthorized access.
Site Disclaimer
WiperSoft.com is not sponsored, affiliated, linked to or owned by malware developers or distributors that are referred to in this article. The article does NOT endorse or promote malicious programs. The intention behind it is to present useful information that will help users to detect and eliminate malware from their computer by using WiperSoft and/or the manual removal guide.
The article should only be used for educational purposes. If you follow the instructions provided in the article, you agree to be bound by this disclaimer. We do not guarantee that the article will aid you in completely removing the malware from your PC. Malicious programs are constantly developing, which is why it is not always easy or possible to clean the computer by using only the manual removal guide.