Utjg ransomware removal
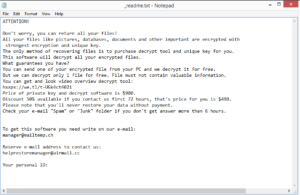
Utjg ransomware is a file-encrypting malware that adds .utjg to encrypted files. This ransomware comes from the notorious Djvu/STOP ransomware family and is the most recent version released by this gang. Ransomware versions from this family are considered to be quite dangerous because there is no free decryptor to decrypt encrypted files. The malware operators will offer you a decryptor for $980 but paying is not a good idea for a couple of reasons.
Utjg comes from the same cybercrime gang responsible for Futm, Qmak, Qdla, and Irfk. These versions are more or less identical but can be differentiated by the extensions they add to encrypted files. This ransomware adds .utjg, which is why it’s named Utjg ransomware. Like most ransomware, it will target personal files, including photos, images, videos, documents, etc. Encrypted files will have .utjg attached to them. For example, image.jpg would become image.jpg.utjg. You will not be able to open any of these files unless you first run them through a decryptor. Unfortunately, the only working decryptor is in the hands of the people operating this ransomware. They will try to sell it to you, however. The whole process of how to acquire the decryptor will be explained in the _readme.txt ransom note that gets dropped in all folders that contain encrypted files. The note explains that to get the decryptor, victims need to pay a ransom. The price for the decryptor is $980, though supposedly if victims make contact within the first 72 hours, the price would be lowered to $490.
Generally, paying the ransom is not encouraged. Primarily because there are no guarantees that a decryptor will actually be sent to you even after you pay. Keep in mind that you are dealing with a cybercrime gang and there’s very little obligating them to actually keep their end of the deal. Unfortunately, many people paid the ransom but received nothing in return in the past. So while whether to pay or not is your decision, we feel it’s necessary to warn you about the risks. Furthermore, the reason ransomware is thriving is because victims keep paying the ransom. The whole business brings cybercriminals a lot of money, and as long as the money keeps flowing into their accounts, they will continue with their malicious activities.
If you have a backup of files, you can safely recover them as long as you make sure to first fully remove Utjg ransomware from the computer. Use capable anti-malware software to do the job, and once the ransomware is gone, connect to your backup to recover files. Do not attempt to delete Utjg ransomware manually because you could end up causing even more damage.
If you do not have a backup, back up encrypted files and wait for a free decryptor to be released. While you will not find one now, it could be released in the future. Unfortunately, developing one is tricky because ransomware infections from this family use online keys to encrypt files. That means that each user has a unique key and that key is necessary to decrypt files encrypted with that specific key. Until the mass keys are released by either the cybercriminals themselves or law enforcement, a universal decryptor is unlikely to be released. But it’s not impossible. Thus, keep the encrypted files safe and occasionally check NoMoreRansom for a free decryptor. If you have already looked for a decryptor, you may have come across the free Djvu/STOP decryptor by Emsisoft. It’s unlikely to work on versions released after 2019 but there is no harm in trying. And keep in mind that there are many fake decryptors on the Internet, ones that could result in more malware on your computer. If you cannot find a decryptor on legitimate sites like NoMoreRansom, the decryptor you encounter on a questionable forum is unlikely to be safe.
How to avoid a ransomware infection
When it comes to malware infections, users with bad online habits have a much higher chance of picking up some kind of malware infection. If you open unsolicited email attachments without first checking them for malware, download copyrighted content via torrents, click on ads while visiting high-risk websites, etc., it’s no wonder that your computer got infected with some kind of malware.
Emails carrying malware are one the most common and effective ways to distribute malware. It requires little effort, as cybercriminals only have to purchase email addresses from hacker forums to launch their malicious campaigns. Fortunately for users, these malicious email campaigns are often quite noticeable, primarily because they do not target anybody specific but rather users on a larger scale. This means the emails are very generic, making them easy to spot. One of the most obvious signs of a malicious email is grammar and spelling mistakes. If you receive an email, seemingly from someone whose services you use, take note of whether there are grammar/spelling mistakes. Keep in mind that legitimate emails from such companies will not have such mistakes because they appear unprofessional. Another thing to take note of is the way an email addresses you. If an email from a sender who should know your name addresses you as “Customer”, “User”, “Member”, etc., it’s likely that you are dealing with a malicious sender impersonating a legitimate one. Lastly, because some malicious emails are more sophisticated than others, we recommend scanning all unsolicited email attachments with anti-virus software or VirusTotal.
Another common way users pick up malware infections is via torrents. It’s no secret that torrent sites are very poorly regulated, which can allow malicious actors to upload malicious content disguised as torrents for movies, TV shows, video games, software, etc.
Utjg ransomware removal
Do not attempt to recover files from backup until you completely remove Utjg ransomware from your computer. If the ransomware is still present when you connect to your backup, those files would become encrypted as well. Use anti-malware software to delete Utjg ransomware because it’s a complicated malware infection and you should not attempt to do it manually. Incorrectly removing a malware infection could result in additional damage.
Site Disclaimer
WiperSoft.com is not sponsored, affiliated, linked to or owned by malware developers or distributors that are referred to in this article. The article does NOT endorse or promote malicious programs. The intention behind it is to present useful information that will help users to detect and eliminate malware from their computer by using WiperSoft and/or the manual removal guide.
The article should only be used for educational purposes. If you follow the instructions provided in the article, you agree to be bound by this disclaimer. We do not guarantee that the article will aid you in completely removing the malware from your PC. Malicious programs are constantly developing, which is why it is not always easy or possible to clean the computer by using only the manual removal guide.